The economic impact of streaming Platforms
The Economic Impact of Streaming Platforms
In the last decade, streaming platforms have emerged as one of the most influential forces in the global entertainment industry. From Netflix and Amazon Prime Video to Disney+, Hulu, and regional services like India’s Hotstar and Japan’s U-Next, the way content is produced, distributed, and consumed has undergone a dramatic transformation. This shift has had profound economic implications, affecting not only the media and entertainment industries but also adjacent sectors such as technology, telecommunications, and advertising. This article explores the multifaceted economic impact of streaming platforms, examining how they generate revenue, influence employment, reshape consumer behavior, and disrupt traditional models of content distribution.
1. The Rise of Streaming: A Market Overview
Streaming services have seen explosive growth in subscriber numbers and revenues. According to Statista, global revenue from video streaming reached approximately $95 billion in 2023 and is projected to surpass $137 billion by 2027. Netflix alone boasts over 260 million subscribers worldwide. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of streaming, as lockdowns forced consumers to turn to home entertainment.
The shift from linear television and physical media to on-demand digital platforms has created a new ecosystem. This system is driven by subscription-based video on demand (SVOD), advertising-based video on demand (AVOD), and hybrid models that combine both. Each model has its own economic dynamics, offering unique opportunities and challenges.
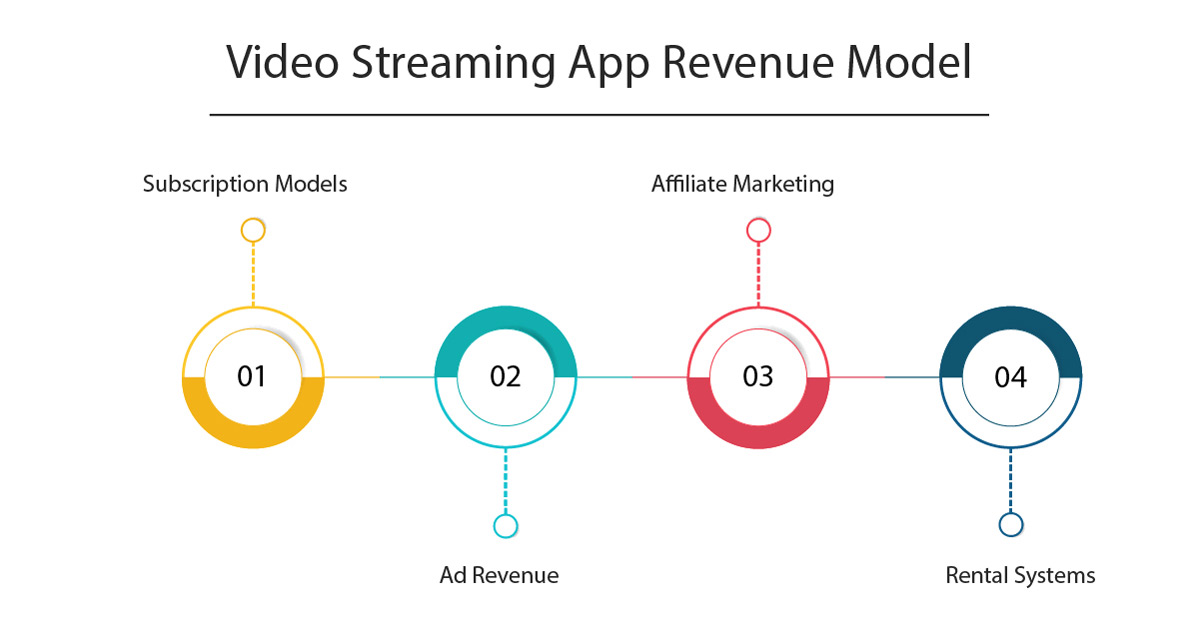
2. Revenue Models and Monetization
Streaming platforms utilize diverse revenue models:
a. Subscription-Based (SVOD): Services like Netflix and Disney+ rely on monthly subscriptions. Revenue scales with user base and is relatively predictable, which appeals to investors and content creators.
b. Advertising-Based (AVOD): Platforms like Pluto TV and YouTube monetize through advertisements. AVOD is growing rapidly, particularly in emerging markets where users are price-sensitive.
c. Transactional Video on Demand (TVOD): Users pay for individual pieces of content, as seen on iTunes or Amazon’s rent/buy model.
d. Freemium Models: Some platforms offer a basic version for free with ads and a premium ad-free experience for a fee, such as Spotify in music streaming.
These models have opened up new revenue streams and allowed content providers to reach audiences previously inaccessible through traditional distribution.
3. Employment and Job Creation
The streaming boom has led to significant job creation across various domains:
-
Content Production: With the "streaming wars" intensifying, platforms are investing billions in original content. This fuels demand for writers, directors, producers, editors, and technical crew.
-
Technology and Data Analytics: Streaming relies heavily on tech infrastructure. Engineers, data scientists, and UX designers play a critical role in optimizing performance and personalization.
-
Marketing and Distribution: The need to attract and retain subscribers creates demand for digital marketing specialists, social media managers, and campaign strategists.
In 2022 alone, Netflix invested over $17 billion in content, directly supporting thousands of jobs. The ripple effect also boosts employment in local economies where filming takes place.
4. Disruption of Traditional Media Models
Streaming platforms have upended the traditional cable TV and film industries:
-
Cord Cutting: A growing number of consumers are cancelling cable subscriptions in favor of streaming services, leading to revenue declines for traditional broadcasters.
-
Theatrical Releases vs. Direct-to-Streaming: Studios now release films directly on streaming platforms, bypassing cinemas. This model challenges the financial viability of theaters but increases accessibility.
-
Syndication and Licensing: Shows that once relied on syndication now find second lives on platforms like Hulu or HBO Max, often generating new revenue long after initial release.
This disruption has forced traditional players to adapt, resulting in mergers (e.g., Warner Bros. Discovery), the launch of proprietary streaming services, and investment in digital transformation.
5. Changing Consumer Behavior and Global Reach
Streaming platforms have democratized access to content:
-
On-Demand Convenience: Users can watch content anytime, on any device, increasing engagement and time spent on platforms.
-
Binge-Watching Culture: Full-season releases encourage binge-watching, influencing narrative structures and viewer expectations.
-
Global Content Consumption: Korean dramas, Spanish thrillers, and Indian documentaries now find global audiences, thanks to subtitling and dubbing. This fosters cultural exchange and cross-border revenue generation.
Consumer behavior data also allows platforms to tailor recommendations, create hit shows based on preferences, and refine their monetization strategies.
6. Economic Impact on Adjacent Industries
The influence of streaming goes beyond entertainment:
-
Telecommunications: The demand for high-speed internet has soared, prompting infrastructure investments by telecom companies.
-
Smart Devices: The popularity of smart TVs, tablets, and streaming sticks (like Roku and Chromecast) has risen, boosting the consumer electronics market.
-
Cloud Services: Platforms rely on cloud computing for content delivery, benefiting companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.
-
Merchandising and Licensing: Successful streaming shows spawn merchandise lines, video games, and spin-offs, contributing to the economy in multiple sectors.
7. Challenges and Criticisms
Despite their success, streaming platforms face several economic and ethical challenges:
-
Content Saturation: With thousands of shows available, discoverability becomes difficult. Smaller productions may struggle to gain visibility.
-
Labor Disputes: The rise of streaming has raised concerns about fair compensation for creatives, especially writers and actors. The 2023 Hollywood writers' strike, for instance, was driven by streaming-related issues.
-
Data Privacy and Algorithmic Bias: Monetization through data can lead to privacy concerns and algorithmic echo chambers.
-
Global Inequality: While developed countries enjoy easy access to streaming, infrastructural and economic barriers limit reach in less developed regions.
8. The Future Outlook
The streaming industry is evolving rapidly:
-
Consolidation: Smaller platforms may merge or get acquired due to competitive pressure and content costs.
-
Diversification: Platforms are branching into live sports, gaming, and interactive content to attract new demographics.
-
Tiered Pricing and Bundling: To combat subscription fatigue, companies may introduce flexible pricing and bundle services (e.g., Disney+, Hulu, and ESPN+ packages).
-
Localized Content: Investment in regional content will grow to cater to non-English-speaking markets and drive international growth.
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven content generation and virtual production (like LED walls) may further revolutionize the cost and scale of content creation.
Conclusion
Streaming platforms have fundamentally transformed the entertainment economy. They have generated new revenue streams, empowered global creators, and reshaped consumer expectations. While they bring innovation and economic opportunities, they also disrupt long-standing models and pose challenges related to equity, labor, and regulation. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the economic landscape of streaming. Policymakers, creators, and companies must navigate this dynamic environment thoughtfully to ensure that the benefits of the streaming revolution are inclusive and sustainable.
The streaming era is not just a shift in how we watch—it's a major economic force shaping the present and future of global media.








Comments
Post a Comment